1 Display loading
1.1 Display loading
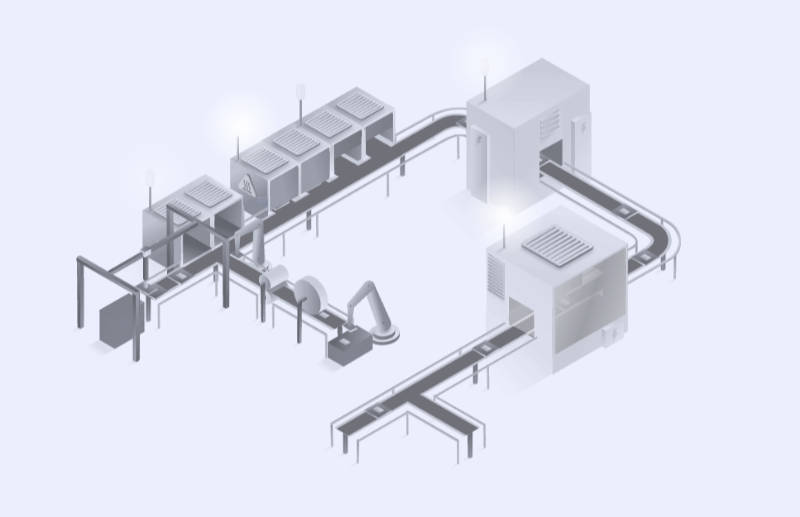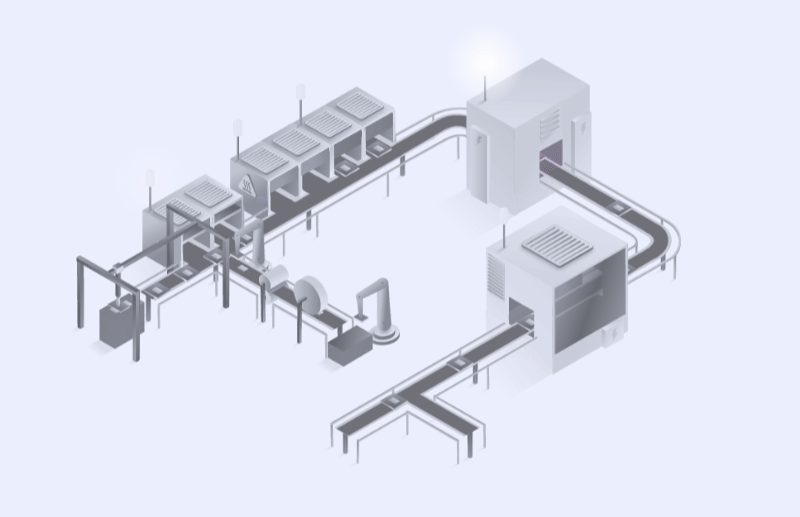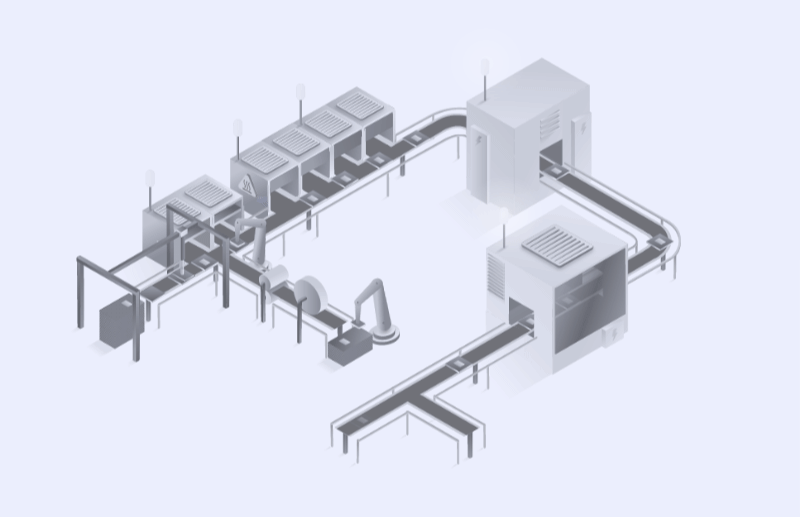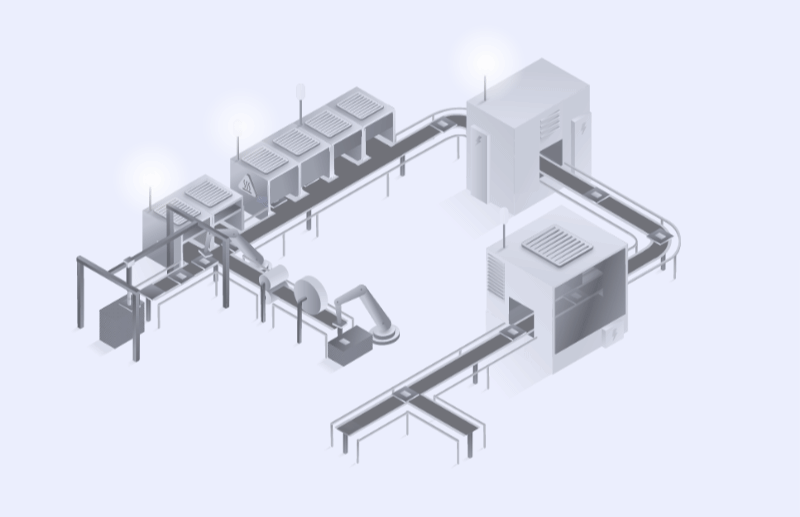
When display packaging is suitable for automation, robots are employed to load production lines. The advantages of robotic loading include consistent precision, increased speed, continuous operation, reduced labor costs, improved safety, and the ability to collect and analyze data for process optimisation. Robots also provide scalability and space efficiency. However, there are significant initial setup and maintenance costs associated with automated packing systems. As technology continues to evolve, robots may be able to handle more tasks currently assigned to humans.
On the other hand, manual loading is used when material packaging is not suitable for automation or when robots' vision systems cannot accurately detect the position and orientation of components due to issues like low color contrast between packaging and products. Human operators are effective in these scenarios, adapting to changing production demands, making decisions based on visual indicators, and offering dexterity that machines might not have. While the initial cost of human labor might be lower than robotic automation, long-term economic factors and the human cost of repetitive automateable tasks should be considered. The choice between robotic and manual loading ultimately depends on specific production requirements.